As defined by Wikipedia Cultural heritage is the legacy of tangible and intangible heritage assets of a group or society that is inherited from past generations.
Cultural heritage includes tangible culture (such as buildings, monuments, landscapes, books, works of art, and artifacts), intangible culture (such as folklore, traditions, language, and knowledge), and natural heritage (including culturally significant landscapes, and biodiversity).
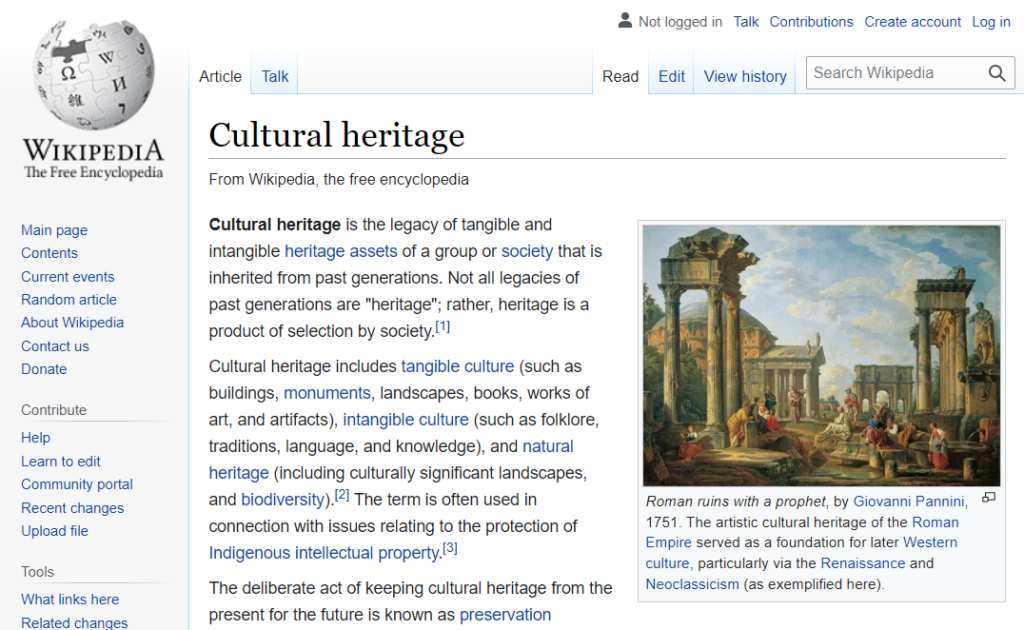
Roman ruins with a prophet, by Giovanni Pannini, 1751. The artistic cultural heritage of the Roman Empire served as a foundation for later Western culture, particularly via the Renaissance and Neoclassicism (as exemplified here).
Tangible Heritage
Tangible Heritage includes the physical cultural heritage, such as artworks. These are generally split into two groups of movable and immovable heritage. Immovable heritage includes buildings (which themselves may include installed art such as organs, stained glass windows, and frescos), large industrial installations, residential projects or other historic places and monuments. Moveable heritage includes books, documents, moveable artworks, machines, clothing, and other artifacts, that are considered worthy of preservation for the future. These include objects significant to the archaeology, architecture, science or technology of a specified culture (source: Wikipedia).
Intangible Heritage
Intangible cultural heritage” consists of non-physical aspects of a particular culture, more often maintained by social customs during a specific period in history. The concept includes the ways and means of behavior in a society, and the often formal rules for operating in a particular cultural climate. These include social values and traditions, customs and practices, aesthetic and spiritual beliefs, artistic expression, language and other aspects of human activity (source: Wikipedia) .
The Grandfather tells a story, by Albert Anker, ca. 1884.
The Grandfather tells a story, by Albert Anker, ca. 1884.
Intangible Heritage
Intangible cultural heritage” consists of non-physical aspects of a particular culture, more often maintained by social customs during a specific period in history. The concept includes the ways and means of behavior in a society, and the often formal rules for operating in a particular cultural climate. These include social values and traditions, customs and practices, aesthetic and spiritual beliefs, artistic expression, language and other aspects of human activity (source: Wikipedia) .
World Heritage Flag, by Holger.Ellgaard , CC BY-SA 3.0
World Heritage
Tangible and the intangible heritage can be listed as national heritage in their related countries but when they are considered very important for the humanity they can be listed by the UNESCO as a world heritage and will be under a legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO.
UNESCO have several conventions and recommendations to protect the world heritage including:
- The Convention concerning the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage was adopted by the General Conference of UNESCO on 16 November 1972.
- The Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage adopted by the UNESCO General Conference on 17 October 2003.
- The Recommendation concerning the preservation of, and access to, documentary heritage including in digital form, adopted by the UNESCO General Conference in November 2015.
World Heritage covers several categories that falls into the scope of the Wiki World Heritage User Group. The main categories that we are covering are: